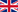
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) is a technique in which an enteral nutrition tube is inserted through the abdominal wall, in direct communication with the patient's stomach, so that a new nutrient entry door is created, liquids and medications The method used is an endoscopic procedure, which allows advantages over other methods used (interventional radiology with percutaneous approach), since it allows direct vision of the stomach and the possibility of verifying that the probe has been placed correctly.
It is a flexible tube, usually made of silicone, with a distal end that is anchored in the gastric cavity, by means of a balloon, or a rounded retaining ring to avoid possible injuries or involuntary extractions. The proximal end contains one or two connections (depending on the type of probe) that adapt to the syringes or infusion pumps to administer the desired formula.
Indications.
The objective of the placement of the PEG, is to maintain an adequate nutritional status in people who, due to their characteristics, physical or mental, cannot feed normally through the mouth, usually by long-term pathological processes:
• Neurological diseases that cause swallowing problems, such as dementias, stroke, head trauma, Guillam-Barré, etc.
• Neoplastic diseases of the oropharynx, larynx and esophagus.
• Patients with facial trauma.
• Mechanical obstructions or partial failure of intestinal function.